Rocky Linux with Cloud-Init
Previously, I made a Debian unattended installer with preseed. I wanted to try out a RHEL-based OS for some projects, so I chose Rocky Linux.
Setup
Create a sample VM (Proxmox is my hypervisor) for the template, but don’t add a cloud-init drive yet. Then just install Rocky Linux 9.0 normally. I wouldn’t create a user here, and just set a root password.
Here I noticed that I really dislike the installer for RHEL-based systems. I don’t like having to move my mouse so much inside a VM. Also, it doesn’t let me use GPT on Legacy systems at all, it forces you to use the MSDOS label, so I ended up just using UEFI. But that’s just another reason to create a template like this!
Then install the packages you want, qemu-guest-agent, etc.
Install cloud-init and enable all the services:
dnf install cloud-init
systemctl enable cloud-init-local
systemctl enable cloud-init
systemctl enable cloud-config
systemctl enable cloud-finalDon’t start it now, because we want to configure it still.
Then, edit the cloud config file /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg to your liking. Here is mine:
users:
- default
disable_root: 1
ssh_pwauth: 0
mount_default_fields: [~, ~, 'auto', 'defaults,nofail,x-systemd.requires=cloud-init.service,_netdev', '0', '2']
resize_rootfs_tmp: /dev
ssh_deletekeys: 1
ssh_genkeytypes: ['rsa', 'ecdsa', 'ed25519']
syslog_fix_perms: ~
disable_vmware_customization: false
cloud_init_modules:
- disk_setup
- migrator
- bootcmd
- write-files
- growpart
- resizefs
- set_hostname
- update_hostname
- update_etc_hosts
- rsyslog
- users-groups
- ssh
cloud_config_modules:
- mounts
- locale
- set-passwords
- rh_subscription
- yum-add-repo
- package-update-upgrade-install
- timezone
- puppet
- chef
- salt-minion
- mcollective
- disable-ec2-metadata
- runcmd
cloud_final_modules:
- rightscale_userdata
- scripts-per-once
- scripts-per-boot
- scripts-per-instance
- scripts-user
- ssh-authkey-fingerprints
- keys-to-console
- phone-home
- final-message
- power-state-change
system_info:
default_user:
name: sysconf
lock_passwd: true
gecos: Very Good Sysadmin
groups: [adm, systemd-journal]
sudo: ["ALL=(ALL) ALL"]
shell: /bin/bash
distro: rhel
paths:
cloud_dir: /var/lib/cloud
templates_dir: /etc/cloud/templates
ssh_svcname: sshd
# vim:syntax=yamlThe biggest change I made was in the default_user section. I changed the name and gecos, and I made sudo prompt for a password every time. I tried locking the root password with:
users:
- name: root
lock_passwd: truebut failed.
Once you’ve configured everything to your liking, you can just shut down (with shutdown now). Then in Proxmox, enable QEMU guest agent if you installed it, and add a cloud-init drive. Finally, you could clone it to test it.
Troubleshooting
You probably won’t get the perfect config every time, but it isn’t as straightforward to retry. When booting, you need to press e with your GRUB entry selected, to edit the kernel command line:
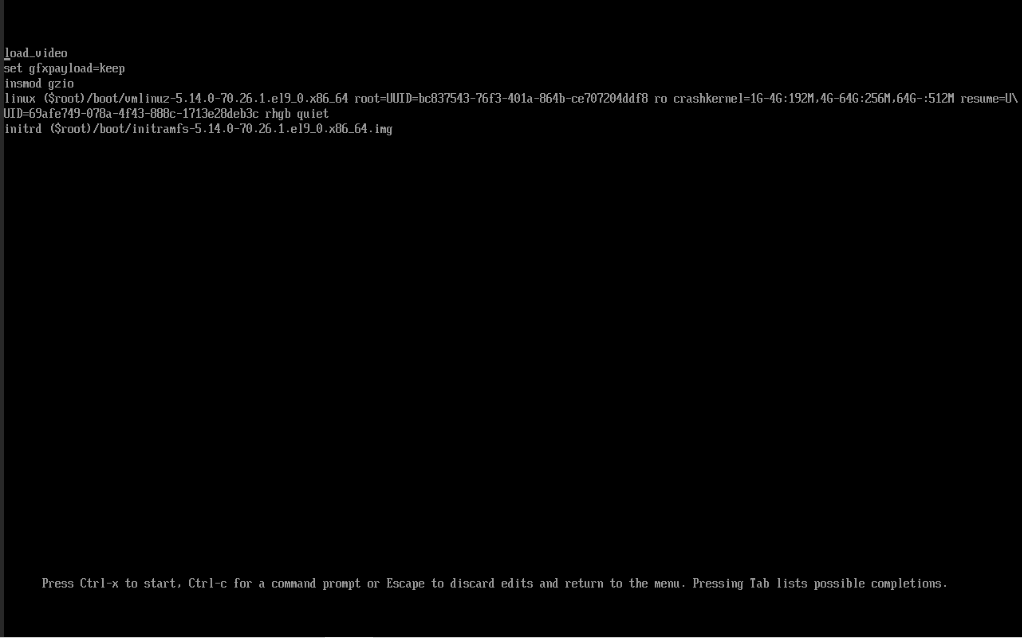
At the linux line, add a cloud-init=disabled to the end:
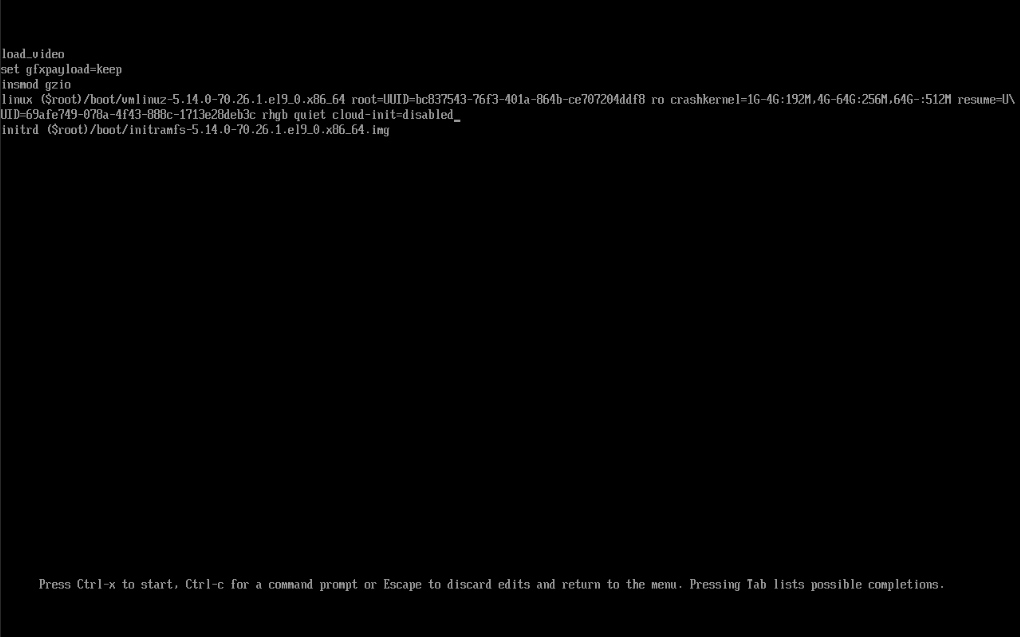
Then it will boot without cloud-init, so you can make changes safely.
Conclusion
You could make the VM as a Proxmox template if you want. But this makes it so you can’t start it easily. You could edit the VM config file manually to make it not a template, but I don’t know whether that messes with it or not. It would be helpful to make it not startable, so you don’t accidentally run cloud-init on it, but I haven’t figured that out yet.
I initially tried to make cloud-init with FreeBSD, but I failed, so I decided to try a more supported OS to become more familiar with cloud-init. This has definetely helped, so I look forward to making cloud-init work in the future.
Docker Pitfalls
Windows Installer USB on macOS